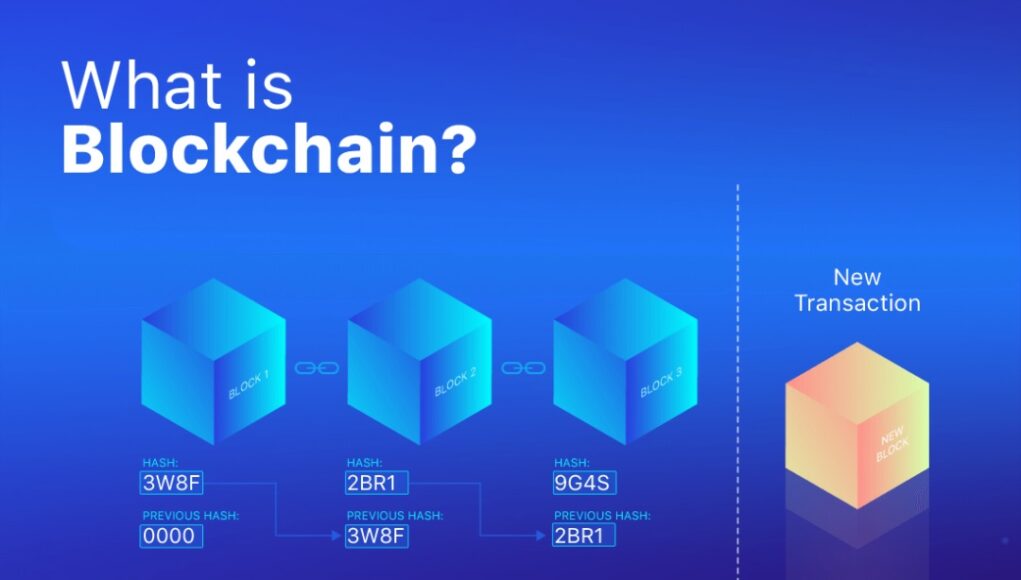
Blockchain technology serves as a decentralized and immutable ledger, which records transactions and information across a network of computers. This transparent and tamper-proof nature of blockchain makes it an ideal tool for addressing the issues of provenance and intellectual property in the art world.
Blockchain Technology – Ensuring Authenticity and Provenance:
Provenance, or the documented history of an artwork’s ownership, has long been a critical factor in determining its authenticity and value. However, the conventional art market has faced challenges in maintaining reliable and transparent provenance records. With blockchain, each transaction involving an artwork can be recorded in a secure and unalterable manner. This ensures that the ownership history of a piece can be easily traced back to its origin, providing collectors and buyers with verified information about its authenticity and lineage.
Protecting Copyright and Intellectual Property:
Intellectual property rights are a cornerstone of the art world, safeguarding artists’ creative expressions and granting them exclusive control over their works. Unfortunately, unauthorized copying and distribution of artworks have been persistent issues, leading to financial losses and the dilution of artistic value.
By leveraging blockchain technology, artists can securely register their creations and establish a digital certificate of authenticity. This certificate can include crucial information such as copyright details, provenance, and licensing terms. As a result, blockchain offers a robust mechanism to protect artists’ rights and ensure fair compensation for their work, discouraging plagiarism and unauthorized reproduction.
Entertainment Industry: Empowering Content Creators
Blockchain can empower content creators in the entertainment industry by enabling direct peer-to-peer interactions and fair monetization of their work. Smart contracts can ensure automatic royalty payments, eliminating intermediaries and promoting a more equitable distribution of profits.
In the rapidly evolving landscape of the entertainment industry, content creators play a vital role in shaping the narratives that captivate and engage audiences worldwide. However, traditional systems have often marginalized these creators, leaving them with limited control over their work and uncertain compensation.
With the emergence of blockchain technology, there is now an unprecedented opportunity to empower content creators, foster direct peer-to-peer interactions, and revolutionize the monetization process. This article explores how blockchain can transform the entertainment industry, offering creators a more equitable and transparent ecosystem for their artistic endeavors.
Direct Peer-to-Peer Interactions:
Blockchain technology facilitates direct peer-to-peer interactions, eliminating the need for intermediaries that have traditionally controlled the distribution and monetization of content. Content creators can now connect directly with their audience, fostering a stronger sense of community and engagement. By leveraging blockchain-powered platforms, creators can share their work, receive feedback, and build a loyal fan base, leading to enhanced creativity and collaboration.
Intellectual Property Protection:
Intellectual property (IP) protection is a crucial aspect of content creation, as unauthorized use or distribution can undermine the value and integrity of a creator’s work. Blockchain technology can provide an immutable and tamper-proof record of ownership and copyright information.
By timestamping and storing digital content on the blockchain, creators can establish irrefutable proof of authorship and safeguard their intellectual property rights. This not only helps combat piracy but also enhances the confidence of content creators in sharing their work with the world.
Enhanced Funding Opportunities:
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize funding models in the entertainment industry. Through the use of tokenization and decentralized crowdfunding platforms, creators can get the right of entry to an international pool of buyers who agree with their vision.
This opens up new avenues for financing projects, reducing reliance on traditional gatekeepers and empowering creators to pursue their artistic ambitions. Tokenization also enables fractional ownership, allowing fans and investors to share in the success of a project and creating a stronger sense of community engagement.
Data Transparency and Audience Insights:
The entertainment industry thrives on understanding audience preferences and behavior. Blockchain technology can facilitate data transparency while ensuring privacy and security. Content creators can access granular insights into their audience’s consumption patterns, preferences, and feedback without compromising individual privacy. This data-driven approach allows creators to make informed decisions, tailor their content to audience demand, and forge stronger connections with their fan base.
Challenges and Limitations:
Despite its immense potential, blockchain technology faces challenges and limitations. Scalability, energy consumption, regulatory frameworks, and public acceptance are key areas that require further development and collaboration to unlock the full potential of blockchain across industries.
Scalability:
One of the primary challenges faced by way of blockchain technology is scalability. Traditional blockchains, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, have limitations in terms of the number of transactions they can process per second. As the popularity of blockchain grows and more users join the network, the transaction processing capacity becomes a bottleneck. Solving the scalability issue is crucial for blockchain to be widely adopted and integrated into various industries.
Energy Consumption:
Another significant concern associated with blockchain technology is its energy consumption. Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus algorithms, used by many blockchains, require extensive computational power and energy to validate transactions and secure the network.

This energy consumption has raised environmental concerns, especially considering the increasing number of blockchain networks and their growing energy requirements. Developing more energy-efficient consensus algorithms or transitioning to alternative consensus mechanisms can help address this limitation.
Regulatory Frameworks:
Blockchain technology operates across borders, making it challenging to establish uniform regulatory frameworks. Governments and regulatory bodies are still grappling with understanding and defining the legal and regulatory aspects of blockchain and cryptocurrencies.
The absence of clear regulations can create uncertainty for businesses and hinder the widespread adoption of blockchain technology. Collaborative efforts between industry stakeholders, policymakers, and regulators are necessary to establish a balanced and effective regulatory framework.
Public Acceptance:
Despite the potential benefits of blockchain technology, its widespread adoption by the general public remains a challenge. Blockchain is a complex technology, and understanding its intricacies can be daunting for many individuals.
Additionally, concerns related to privacy, security, and the association with illicit activities have led to skepticism and resistance among some segments of the population. Educating the public about blockchain, addressing security concerns, and highlighting the advantages of decentralized systems are crucial steps to foster public acceptance and trust.
Interoperability:
Interoperability refers to the capacity of different blockchain networks to speak and share information seamlessly. Currently, most blockchains operate in isolation, hindering the exchange of assets and information between different networks.
Achieving interoperability would enable the integration of various blockchain platforms, enhancing their overall functionality and expanding the potential use cases. Developing standardized protocols and frameworks for interoperability is a significant challenge that requires collaboration and coordination between blockchain projects.
Privacy and Security:
While blockchain technology is known for its transparency and immutability, ensuring privacy and security within the blockchain ecosystem is a critical concern. Public blockchains store all transaction data on the ledger, making it accessible to anyone.
While this transparency has its advantages, it poses challenges when dealing with sensitive information. Finding a balance between transparency and privacy, implementing robust encryption mechanisms, and addressing potential vulnerabilities and attacks are essential for blockchain’s broader adoption.
User Experience:
User experience plays a vital role in the adoption of any technology. Blockchain interfaces and interactions can often be complex and confusing for the average user. Improving the user experience by developing intuitive interfaces, simplifying wallet management, and providing user-friendly applications can help bridge the gap between blockchain technology and mainstream users. Usability-focused development and design practices can make blockchain more accessible and user-friendly.
Legacy System Integration:
Integrating blockchain technology with existing legacy systems poses a significant challenge for many industries. Many organizations rely on legacy infrastructure and processes that may not be easily compatible with blockchain solutions.
Transitioning from centralized systems to decentralized blockchain networks requires careful planning, coordination, and overcoming technical barriers. Developing seamless integration solutions and providing support for legacy system migration is necessary for the wider adoption of blockchain technology.
Addressing these challenges and limitations will require ongoing collaboration and innovation from various stakeholders, including technology developers, businesses, governments, and the general public. As blockchain technology continues to evolve and mature, overcoming these obstacles will unlock its full potential and pave the way for a decentralized and transparent future.

















