In recent years, blockchain technology has gained widespread attention primarily due to its association with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. Nevertheless, blockchain capabilities far surpass the boundaries of digital currencies.
This article delves into blockchain technology’s various applications and possibilities, highlighting its transformative power in diverse industries.
Understanding Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is a distributed, open-source ledger that keeps track of transactions on numerous computers. It works on a peer-to-peer network, ensuring security, immutability, and trust. Each transaction is grouped into a “block”; and added to the chain of previous transactions, creating a historical record.
Benefits Of Blockchain Technology Offers Several Benefits That Make It Attractive To Many Industries:
Key Benefits Include:
Transparency: Blockchain provides transparent and verifiable transaction records, allowing for better accountability and traceability.
Security: The decentralized nature of the blockchain makes it highly secure as data is stored on multiple nodes, reducing the risk of hacking or fraud.
Efficiency: Blockchain eliminates intermediaries, streamlines processes, and reduces costs.
Data Integrity: Once transactions are recorded on the blockchain, they cannot be altered, ensuring data integrity and accuracy.
Trust: Blockchain creates trust among participants by providing an auditable and immutable record of transactions.
The Fundamentals of Blockchain Technology
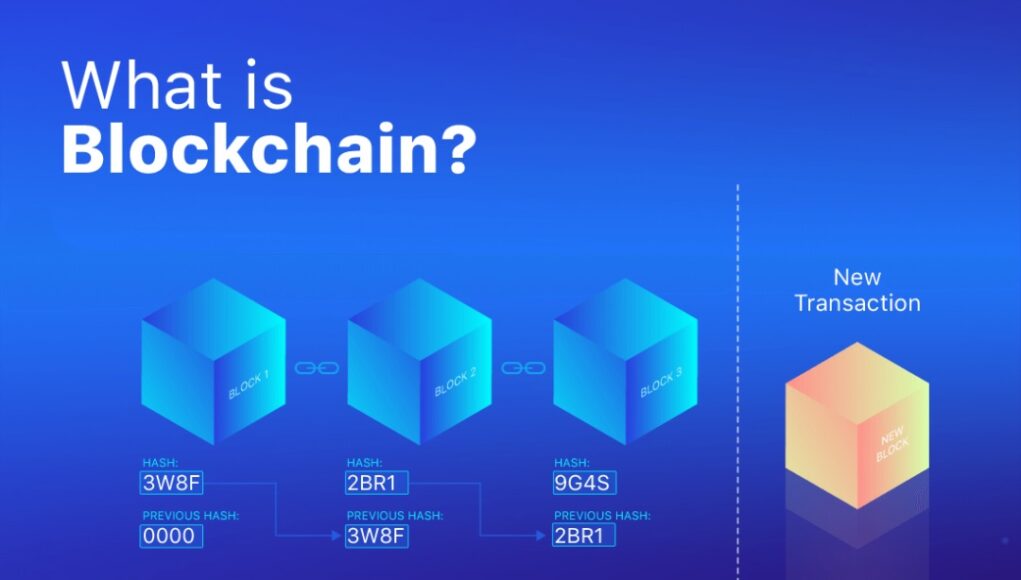
In the world of digital record-keeping, blockchain emerges as a remarkable decentralized and unchanging ledger that meticulously logs transactions across numerous computers or nodes. Within this blockchain structure, each block encompasses a specific data collection accompanied by a distinct identifier known as a hash. Such a design guarantees utmost security and preserves the integrity of the stored information, making it virtually tamper-proof.
Blockchain Beyond Cryptocurrencies
Blockchain technology has become increasingly prominent, not only in the realm of cryptocurrencies but also in various other industries. Its decentralized and transparent nature has paved the way for transformative applications. In this article, we will explore some exciting use cases where blockchain revolutionizes traditional systems and processes.
One of the areas where blockchain is making its mark is supply chain management. By leveraging blockchain’s immutable and transparent ledger, participants in the supply chain can trace the journey of goods and verify their authenticity at every stage. This increased visibility helps eliminate counterfeit products, reduce fraud, and ensure ethical sourcing practices. Furthermore, blockchain enables automated smart contracts and streamlined payment processes, enhancing efficiency and trust between stakeholders.
Healthcare Sector
Blockchain technology holds immense potential in the healthcare sector, particularly in managing medical records. With blockchain, patient data can be securely stored and accessed only by authorized individuals while maintaining privacy. This decentralized approach eliminates the need for intermediaries, enhances data integrity, and reduces the risk of errors and unauthorized access. Moreover, blockchain can facilitate the interoperability of medical records across different healthcare providers, ensuring seamless and efficient healthcare delivery.
Voting Systems:
Blockchain also offers a robust solution for voting and elections. Traditional voting systems often face fraud, manipulation, and lack of transparency. Blockchain provides a tamper-resistant and transparent platform for conducting elections. By storing votes on a distributed ledger, blockchain ensures the integrity of the voting process. Each vote becomes a permanent record, making altering or manipulating results virtually impossible. This technology can restore public trust in electoral systems and increase participation by enabling remote and secure voting options.
Decentralized Identity Management:
Bneed for centralized authorities. Individuals can securely manage their data using cryptographic techniques, granting access on a need-to-know basis.
In today’s digital age, where personal information is increasingly stored and shared online, there is growing interest in decentralized identity management. Blockchain technology has emerged as a solution, allowing individuals to regain control over their digital identities and promoting privacy, security, and autonomy.
Digital Identities:
Lock chain enables individuals to control their digital identities, eliminating the Traditionally centralized authorities like governments, financial institutions, and social media platforms that have managed and validated individuals’ identities. However, this approach raises concerns such as data breaches, privacy violations, and consolidated power. Consequently, decentralized identity management solutions have gained attention.
Underlying Cryptocurrencies:
Blockchain, the technology underlying cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, forms the basis for decentralized identity systems. Through cryptographic techniques, blockchain enables the secure creation, storage, and validation of digital identities. Instead of relying on a single central authority, power is distributed across a network of computers, making it difficult for malicious actors to tamper with stored identity data.
Self-sovereign identity is a crucial aspect of decentralized identity management. It grants individuals complete control over their personal information and its disclosure. Individuals can securely authenticate themselves using public-private vital pairs and selectively reveal data to authorized parties based on the “need-to-know.” This approach minimizes the risk of data misuse.
Identity Management Systems:
Decentralized identity management systems also enhance privacy. Blockchain-based solutions allow creating pseudonymous identities for different contexts instead of relying on a single identifier, such as a social security number or email address. This enables individuals to engage in online activities without disclosing their identities, reducing the risk of identity theft or profiling.
Privacy and Security:
Beyond privacy and security, decentralized identity management enables seamless portability and interoperability of personal data across platforms and services. Individuals can maintain consistent identities across online interactions, eliminating the need for multiple accounts. Additionally, decentralized identity solutions reduce reliance on third-party intermediaries for identity verification, improving efficiency.
Conclusion:
Despite its promise, decentralized identity management faces challenges. Balancing privacy and accountability is crucial as individuals gain control over their identities. Mechanisms must be established to hold individuals accountable for their actions while safeguarding their privacy rights. Scalability and usability are also important considerations to ensure the widespread adoption of decentralized identity solutions.
















